There are several over heating symptoms that will let you know if the engine is having a problem such as the temperature warning light coming on and noticing the temperature gauge is in the red or close to it. This condition may also be accompanied by a burning coolant smell or reduced engine power. In any case if you think your car's engine is overheating you should safety pull to the side of the road and shut the engine off to avoid internal engine damage.
What Goes Wrong?
The cooling system is used to maintain operational temperatures which have a number of components that can fail or leak coolant due to the constant heat and vibration of the engine. When internal temperatures go beyond their designed capabilities internal damage can occur such as a cracked cylinder head or engine block. One of the most common major failures is a blown head gasket which is used to seal the cylinder head to the engine block and allow coolant to enter either the combustion chamber or the engine oiling system. Further damage can include seized pitons and collapsed piston rings, both will cause low compression and can contribute to the engine not starting after an overheating event.
Let's Jump In!
Always use caution when checking out an engine overheating problem because the cooling system has up to 18 pounds of pressure and is filled with hot coolant which can cause burns. Always allow the engine to cool before testing or inspection.
The cooling system must maintain
pressure and a proper coolant level or the engine will overheat. Wait until the
engine as cooled off and locate and slowly remove the coolant reservoir or radiator
cap and check the coolant level. A small amount of pressure should be released which
is normal if the radiator cap is good. Over time the coolant level can be a little
low which is normal. If the system is continuously low or almost completely out
the cooling system or engine has coolant
leak which needs to be fixed to keep the engine from overheating. If the system
is absent of pressure (you can tell this by squeezing the upper radiator hose and
feel pressure) and the system seems to be full of coolant then the radiator or coolant
reservoir cap needs to be replaced. Some car designs hold pressure in their coolant
reservoir. In these cases the cap will unscrew from the container.

Cooling fans can be either mechanical which are belt driven by the engine, or
electric mounted on the radiator.
Cooling fans are located
directly behind the radiator and are used to move air through the radiator core
which helps remove heat from the coolant at low speeds. If this fan stops operating
the engine will overheat or run hot. To check an electric motor cooling fan, remove
the key from the ignition switch and away from the car. Then reach in and spin the
fan blade by hand, it should "freewheel" and spin easily. If it sounds rough or
is difficult to turn it has gone bad and needs replacement. There is an easy way
to check the electrical portion of the cooling fan system if the
car has air conditioning.
Start the engine and turn the air conditioner to the coldest setting. Within one
minute of the car air conditioner operating the cooling fan(s) should activate.
If the fan does not come on first check
the fuse and then the
relay. If both of these items check out then the
cooling fan motor has most likely
burned out and needs replacement.

If your car is not designed with an electric fan it will have a
thermo fan clutch which is attached
to the water pump and driven by the engine. This device engages and disengages the
fan blade via a temperature sensor at the center of the clutch. When a
fan clutch goes bad it fails to "lock
up" which diminishes the fan blade performance causing the engine to overheat by
allowing the blade to freewheel and not pull air through the radiator. When the
engine is hot this clutch should engage which is followed by a roaring sound as
the fan starts to work. If the engine is hot and you can see the blade freewheeling
while the engine is running the clutch fan
has gone bad and needs replacement.

The engine thermostat
will not allow the coolant to flow into the radiator when the engine is cold. When
the thermostat goes bad it can do so by sticking closed. This means the coolant
never gets a chance to be circulated to the radiator. When this failure occurs the
engine will overheat rapidly usually within the first fifteen minutes of driving
and can be accompanied by a thumping sound as the hot coolant is trying to mix with
the cold coolant in the radiator. Do not open the radiator to check the coolant
level. Allow the engine to cool before replacing
the thermostat.

The radiator is responsible for
dropping the temperature of the engine coolant and can fail in a three different
ways the first is external blockage. Because your car hugs the road it is constantly
being bombarded with debris such as dirt, hair, leaves, trash and bugs to name a
few. Because of this cooling fins can become plugged stopping air flow through the
radiator core causing the engine to overheat. This condition can be hard to detect
because the air conditioner condenser sits in front of the radiator in some cases.
Use a flashlight to help check for blockage and then use a garden hose to pressure
wash the radiator from the backside (facing forward) to help clean and unplug the
radiator.

The second way a radiator can fail is to become plugged internally. To check for
this condition, remove the radiator cap when the engine is cold look inside using
a flashlight. You may need to drain some of the coolant out to see the ends of the
radiator core tubes. In the example below the tubes appear clear with no corrosion
around the end which is what you want. When a radiator plugs internally these tubes
become clogged due to lack of maintenance (radiator
flush) calcium will then stop the coolant flow which inhibits the radiator's
cooling ability. This condition generally occurs gradually over time and will be
more noticeable when climbing a grade or in warmer weather. The third way a radiator
can fail is to leak. This will cause the system to lose coolant and cause overheating.
In either case the radiator must
be replaced.

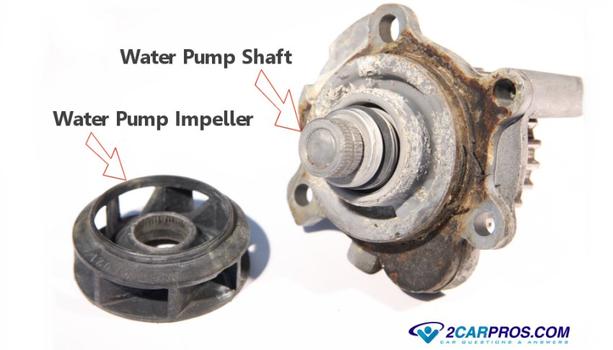
The water or coolant pump is a mechanical
pump which is responsible for circulating coolant throughout the radiator and into
the engine which is driven by the engine serpentine, timing belt or timing chain.
On most hybrid engines this pump is powered by an electric motor.
When a water pump fails it
can do so in one of two ways. First, it can cause a leak which is what happens when
its shaft seal fails or when the shaft bearings fail destroying the seal. This can
sometimes be accompanied by squeaking, squealing, grinding or a rattling sound.
In some instances the impeller of the pump will become dislodged stopping the pumping
action. In either case the water is pump
bad and replacement is required.
A head gasket is used to seal the combustion process within the engine block and cylinder head. This gasket is prone to failure due to natural engine block and cylinder head expansion and contraction as the engine heats up and then cools down. Corrosion due to lack of cooling system maintenance can also play a factor in the gasket's failure. If the block is cast iron and the cylinder head is made of aluminum a process called electrolysis can take place caused by dissimilar metals. This can cause coolant to enter the engine's oiling system and exhaust gasses to be forced into the cooling system which displaces the coolant from the system. This problem is becoming more popular as engine components such as engine blocks and cylinders heads become more lightweight. Fortunately to test for a blown head gasket is a simple process. When this gasket fails it can also cause a rough running engine at start up.
Questions?
Our certified technicians are ready to answer engine overheating questions for free. We hope you saved money and learned from this guide. We are creating a full set of car repair guides. Please subscribe to our 2CarPros YouTube channel and check back often for new videos which are uploaded regularly.


