Hello
Okay, great with the spark. . .. . ...so that is confirmed. As for the pressure. . ..good question. . .
On many vehicles if the car doesn't start in 2 seconds, the fuel pump is turned off. In this case, if the pump is not putting out enough to start the truck then nothing. Also, you may have some pressure at the rail, but that doesn't mean you have enough to run the truck. The regulator keeps the pressure 44.2-54.2 psi. . .. . .anything above 49 the regulator bypasses it back to the tank.
I look at it like a water sprinkler; you may have water coming out of it but not enough pressure to make it turn.
Fuel Pressure
Engine at curb idle 339 ±34 kPa (49.2 ±5 psi)
Pressure Leakdown (fuel pump not engaged) Not fall below 30 psi for 5 minutes
As for the valve stem - I recently had a Tahoe with a fuel pump go out did the same thing. Drove then would die, drove then die. On the way here it quit 100 yards away. Probably not the safest thing, but I took a electric fuel pump I have, put one end into a gas container, took the other end, removed the valve stem on the fuel rail (it still had pressure) and jammed the hose on the end of it. Hooked it up to the battery and the pump was pumping away. I got in the truck, it started right up and drove it on in.
Hope that helps.
I also put the info on the fuel system for your review. It may be say, the regulator, or something else. I just lean to the pump due to the mileage and what it is doing.
Thanks for the update
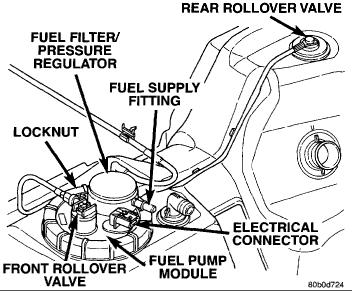
Fuel Pump Module
FUEL PUMP MODULE
The fuel pump module on all gas powered engines is installed in the top of the fuel tank. The fuel pump module contains the following:
A combination fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator
Electric fuel pump
Fuel pump reservoir
A separate in-tank fuel pick-up filter (strainer)
Pressure relief/rollover valve
Fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
Fuel supply line connection
auxiliary non-pressurized fuel supply fitting (not all engines)
FUEL PUMP
The fuel pump used in this system has a permanent magnet electric motor. The pump is part of the fuel pump module. Fuel is drawn in through a filter at the bottom of the module and pushed through the electric motor gearset to the pump outlet.
Check Valve Operation: The pump outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not operational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will remain in fuel supply line between the check valve and fuel injectors. Fuel pressure that has dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle (engine off) is a normal condition. Refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test in this group for more information.
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied through the fuel pump relay.
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a variable resistor (track). The resistor track is used to send electrical signals for both fuel gauge operation and OBD II emission requirements.
For fuel gauge operation: As fuel level increases, the float and arm move up. This decreases the sending unit resistance, causing the fuel gauge to read full. As fuel level decreases, the float and arm move down. This increases the sending unit resistance causing the fuel gauge to read empty.
For OBD II emission requirements: The voltage signal is sent from the resistor track to the Power train Control Module (PCM) to indicate fuel level. The purpose of this feature is to prevent a false setting of misfire and fuel system monitor trouble codes if the fuel level in the tank is less than approximately 15 percent of its rated capacity.
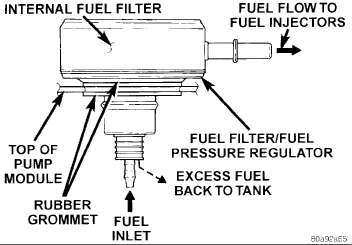
FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
A combination fuel filter and fuel pressure regulator is used on all engines. It is located on the top of the fuel pump module. A separate frame mounted fuel filter is not used with any engine.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for extended service. They do not require normal scheduled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation: The pressure regulator is a mechanical device that is not controlled by engine vacuum or the Powertrain control module (PCM).
The regulator is calibrated to maintain fuel system operating pressure of approximately 339 kPa +/- 34 kPa (49.2 psi +/- 5 psi) at the fuel injectors. It contains a diaphragm, calibrated springs and a fuel return valve. The internal fuel filter (Fig. 3) is also part of the assembly.
Fuel is supplied to the filter/regulator by the electric fuel pump through an opening tube at the bottom of filter/regulator.
The regulator acts as a check valve to maintain some fuel pressure when the engine is not operating.
This will help to start the engine. A second check valve is located at the outlet end of the electric fuel pump. Refer to Fuel Pump-Description and Operation for more information. Also refer to the Fuel Pressure Leak Down Test and the Fuel Pump Pressure Tests.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds approximately 49.2 psi, an internal diaphragm opens and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank through the bottom of pressure regulator.
Monday, November 10th, 2008 AT 3:43 PM





