430 is a bad catalytic converter for bank 2. It is not a sensor at all. It is the precious metals are worn out in the converter.
Bank 2 is the passenger side. They are separate converters.
Circuit Description
This diagnostic test is designed in order to measure the efficiency of the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) system. Catalytic converter efficiency is a measure of its ability to store oxygen after converting the levels of Hydrocarbon (HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) to less harmful gases. The Control Module (PCM/VCM) is able to evaluate the catalyst efficiency once the vehicle has met the enable criteria and the vehicle is at idle instead of steady cruise speeds as in the past. Once the conditions for running this DTC are met, the Control Module commands either a lean or rich air/fuel ratio depending on the current state of the exhaust oxygen level. The Control Module issues a rich command if the exhaust is currently lean, or a lean command if the exhaust is currently rich. After completion of the first command, a second and opposite command is issued.
For example, if the Control Module were to command a rich mixture, the upstream HO2S voltage would increase immediately. The rich mixture is delayed in reaching the downstream HO2S due to the conversion process occurring within the converter. The higher the efficiency, the more the delay before the rich or lean mixture is detected by the downstream O2 sensor. As a result of the lower conversion efficiency within a damaged or poisoned catalyst, the delay in the rich or lean mixture reaching the downstream O2 sensor is significantly shorter. This DTC monitors the amount of time required for both the upstream and downstream HO2S voltages to cross a calibrated voltage threshold in response to the rich or lean command.
Conditions for Running the DTC
No active secondary AIR DTCs
No active CMP sensor DTCs
No active ECT sensor DTCs
No active EGR DTCs
No active fuel trim DTCs
No active IAC DTCs
No active IAT sensor DTCs
No active MAF sensor DTCs
No active MAP sensor DTCs
No active O2 sensor DTCs
No active transmission DTCs
No active EVAP system DTCs
No active TP sensor DTCs
No active VS sensor DTCs
No active misfire DTCs
No active ignition DTCs
The engine speed is 1100 RPM or more for more than 44 seconds since last idle period
The engine has been running for at least 360 seconds and the long term fuel trim is stable
The predicted catalyst temperature is at least 390°C (734°F)
The system is in closed loop
The BARO is 72 kPa or more
The IAT is between -7-75°C (19-167°F)
The ECT is between 75-117°C (167-243°F)
The engine has been idling for less than 120 seconds
The actual engine speed is within 100 RPM of the desired idle speed
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The VCM determines that the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst has degraded below a calibrated threshold
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The Control Module illuminates the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) the first time the diagnostic runs and fails.
The Control Module will set the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The Control Module stores the failure information in the scan tools Freeze Frame and/or the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
The Control Module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has Run and Passed.
A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been dejected for 40 warm-up cycles (coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the start-up coolant temperature and the Engine Coolant Temperature is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle).
Use the scan tool Clear Information function.
Diagnostic Aids
The use of fuel with a high sulfur content or lead can degrade a marginal converters performance. Be sure to check fuel quality.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
A poor connection
Rubbed through wire insulation
A broken wire inside the insulation
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis. See: Computers and Control Systems > Symptom Related Diagnostic Procedures
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
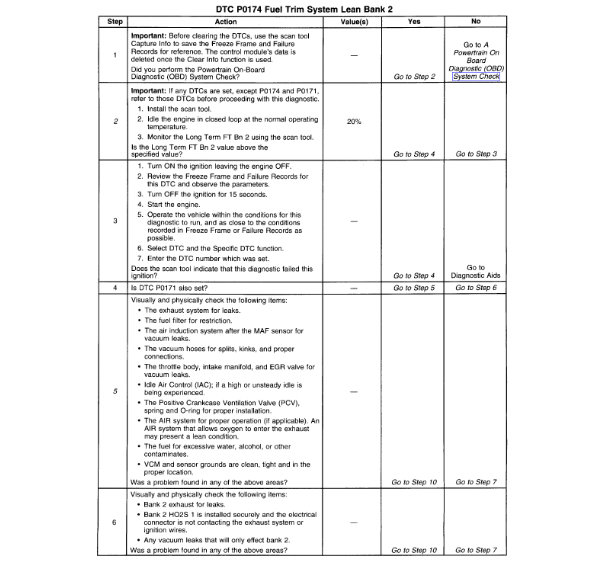
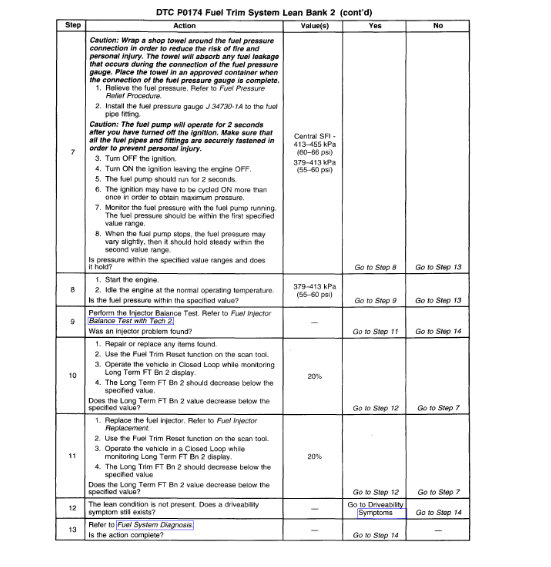
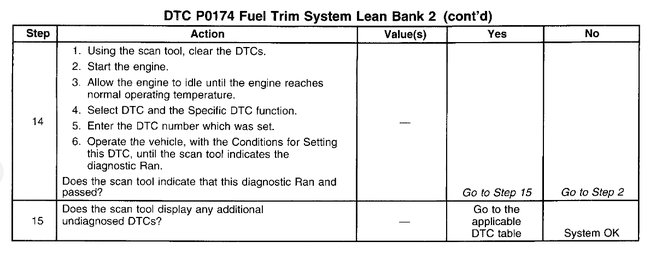
3. This table checks for conditions that can cause the Three-way Catalytic Converter efficiency to appear degraded. Inspect and repair exhaust system as necessary.
6. Before the Three-Way Catalytic Converter is replaced, make sure that the following conditions are not present:
Misfire.
High engine oil consumption or coolant consumption.
Retarded spark timing or weak spark.
Roy
Friday, November 30th, 2018 AT 3:38 PM