Hello .. and thanks for the donation .. much appreciated
You will have to check the whole evap system for leaks .. also check the wiring @ sensor .. let me know
EMISSION SYSTEMS & SUB-SYSTEMS
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
A Three-Way Catalytic (TWC) converter is used to reduce exhaust emissions. This type of converter can reduce Hydrocarbons (HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO) and Oxides Of Nitrogen (NOx).
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM
The Evaporative Emission (EVAP) control system limits fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Fuel tank vapors are allowed to move from the fuel tank, due to pressure in the tank, through the vapor pipe, into the EVAP canister. Carbon in the canister absorbs and stores the fuel vapors. Excess pressure is vented through the vent line and EVAP vent solenoid to atmosphere. The EVAP canister stores the fuel vapors until the engine is able to use them. At an appropriate time, the control module will command the EVAP purge solenoid ON (open), allowing engine vacuum to be applied to EVAP canister. With EVAP vent solenoid OFF (open), fresh air will be drawn through the solenoid and vent line to the EVAP canister. Fresh air is drawn through the canister, pulling fuel vapors from the carbon. The air/fuel vapor mixture continues through the EVAP purge pipe and EVAP purge solenoid into the intake manifold to be consumed during normal combustion. The control module uses several tests to determine if the EVAP system is leaking.
EVAP Canister
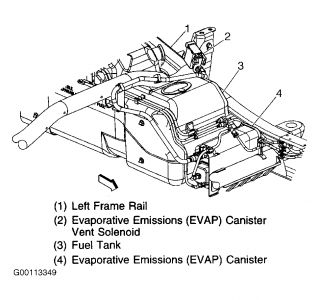
The canister is filled with carbon pellets used to absorb and store fuel vapors. Fuel vapor is stored in the canister until the control module determines that the vapor can be consumed in the normal combustion process. EVAP canister is located near fuel tank. See Fig. 9 .
Fig. 9: Locating EVAP System Canister & EVAP Canister Vent Solenoid
Courtesy of GENERAL MOTORS CORP.
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid
The EVAP canister purge solenoid controls the flow of vapors from the EVAP system to the intake manifold. EVAP canister purge solenoid is located on top of intake manifold. See Fig. 1 . This normally closed solenoid is Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) by the control module to precisely control the flow of fuel vapor to engine. The solenoid will also be opened during some portions of EVAP testing, allowing engine vacuum to enter the EVAP system.
EVAP Canister Vent Solenoid
The EVAP canister vent solenoid controls fresh air flow into the EVAP canister. EVAP canister vent solenoid is mounted on frame rail, near fuel tank. See Fig. 9 . The solenoid is normally open. The control module will command the solenoid closed during some EVAP tests, allowing the system to be tested for leaks.
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor
The Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP) sensor measures the difference between the pressure or vacuum in the fuel tank and outside air pressure. The control module provides a 5-volt reference and a ground to the FTP sensor. The FTP sensor provides a signal voltage back to the control module that can vary between 0.1-4.9 volts. A high FTP sensor voltage indicates a low fuel tank pressure or vacuum. A low FTP sensor voltage indicates a high fuel tank pressure.
Tuesday, January 6th, 2009 AT 1:29 PM




