VISUAL CHECK & EQUIPMENT HOOKUP
Complete all steps in BASIC TESTING article in this section before proceeding to self-diagnostic tests. Ensure vacuum hoses and EEC-IV wiring harnesses are properly connected.
Apply parking brake, and place shift lever in Park (A/T) or Neutral (M/T) position. Block drive wheels. Turn off all electrical accessories. Connect appropriate test equipment to vehicle as follows:
Analog Volt-Ohmmeter (VOM)
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position. Set VOM at 0-15V DC range. Connect positive lead of VOM to positive battery terminal.
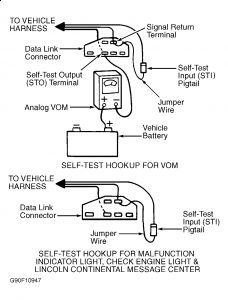
2) Connect negative VOM lead to Self-Test Output (STO) terminal of Data Link Connector (DLC). See Fig. 3 . Connect timing light, and go to KOEO SELF-TEST. Activate KOEO SELF-TEST by connecting jumper wire from Self-Test Input (STI) pigtail to signal return terminal of Data Link Connector (DLC) with ignition on.
Scan Tester
Follow manufacturer's instructions to hook up equipment and record service codes.
STAR Series Tester
Turn ignition switch to OFF position. Connect color-coded adapter cable leads to diagnostic tester. Connect 2 service connectors of adapter cable to vehicle Data Link Connector (DLC) and STI pigtail connector. Connect timing light. Go to KOEO SELF-TEST.
CHECK Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL)
Turn ignition on. Connect a jumper wire between Self-Test Input (STI) pigtail and signal return terminal of Data Link Connector (DLC). See Fig. 3 . Go to KOEO SELF-TEST.
Fig. 3: Connecting Self-Test Equipment
RETRIEVING CODES
Service codes are retrieved from EEC-IV system through Data Link Connector (DLC). Various methods and test equipment may be used to access these codes:
Analog Volt-Ohmmeter (VOM).
Scan tester.
In-Dash Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL)/CHECK ENGINE light.
DATA LINK CONNECTOR (DLC) LOCATIONS
ApplicationLocation
Sable & TaurusRight Rear Of Engine, Below Map Sensor
READING CODES
KOEO & KOER SELF-TEST Codes
PCM outputs codes one digit at a time. Record codes in order received. These codes indicate current faults in system and should be serviced in order of appearance. Use SERVICE CODE-TO-TEST MENUS to find correct CIRCUIT TEST.
If using VOM, pay careful attention to length of pauses in order to read codes correctly. A 1/2-second pause occurs between number of sweeps in a digit. A 2-second pause occurs between digits in a code. A 4-second pause occurs between each code. KOEO codes are separated from Continuous Memory codes by a 6-second delay, a 1/2-second sweep (separator) and another 6-second delay. See Fig. 1 .
If using MIL/CHECK ENGINE light, service codes are displayed as flashes.
Scan tester, if used, will count pulses and display them as a digital code. STAR Series Tester will add a zero (0) to single-digit Separator Code (10) and Dynamic Response Code (10). Dynamic Response Code is displayed in KOER SELF-TEST. See Fig. 1 .
Separator Pulse
Single 1/2-second separator pulse is issued 6-9 seconds after last KOEO code. Continuous Memory Codes (soft faults) are then displayed 6-9 seconds after 1/2-second separator pulse. Some digital test equipment may display separator code as "10" instead of "1".
Pass Codes
A Code 11 or 111 indicates no service codes were recorded in that portion of test; system passes that portion of test. If Code 11 or 111 is not retrieved in KOEO SELF-TEST, codes retrieved during KOER SELF-TEST may not be valid. Code 11 or 111 (pass code) must be obtained in KOEO SELF-TEST. A Code 11-1-11or 111-1-111 output during KOEO SELF-TEST indicates no KOEO code or Continuous Memory Code was recorded.
Continuous Memory Codes
These codes result from information stored by PCM during continuous self-test monitoring. Codes are displayed after separator pulse code in KOEO SELF-TEST. Use these codes for diagnosis only when KOEO SELF-TEST and KOER SELF-TEST result in Code 11 or 111 (pass code) and all steps under QUICK TEST are successfully completed. (A few codes are exceptions which may be checked after KOEO codes have been repaired). These codes indicate faults recorded within last 40 engine starts (80 engine starts on some models). Fault may or may not be currently present. See SERVICE CODE-TO-TEST MENUS.
Fast Codes
At start of KOEO SELF-TEST and after Wide Open Throttle (WOT) request in KOER SELF-TEST, PCM outputs short bursts of information, known as FAST CODES, which were used by manufacturer during assembly. With most equipment, these code bursts are not visible; an entire code sequence lasts less than 1/2 second. If this fluctuation is visible on test equipment, ignore it.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Visually inspect all electrical wiring, looking for chafed, stretched, cut or pinched wiring. Ensure electrical connectors fit tightly and are not corroded. Ensure vacuum hoses are properly routed and are not pinched or cut. See VACUUM DIAGRAMS article in the ENGINE PERFORMANCE Section to verify routing and connections (if necessary). Inspect air induction system for possible vacuum leaks.
MECHANICAL INSPECTION
Compression
Check engine mechanical condition with a compression gauge, vacuum gauge, or an engine analyzer. See engineanalyzer manual for specific instructions. Compression pressures are considered within specifications if the lowest reading cylinder is within 75 percent of the highest reading cylinder.
WARNING:DO NOT use ignition switch during compression tests on fuel injected vehicles. Use a remote starter to crank engine. Fuel injectors on many models are triggered by ignition switch during cranking mode, which can create a fire hazard or contaminate the engine's oiling system.
Exhaust System Backpressure
The exhaust system can be checked with a vacuum or pressure gauge. If using a pressure gauge, remove O2 sensor or air injection check valve (if equipped). Connect a 0-5 psi pressure gauge and run engine at 2500 RPM. If exhaust system backpressure is greater than 2 psi, exhaust system or catalytic converter is plugged.
If using a vacuum gauge, connect vacuum gauge hose to intake manifold vacuum port. Start engine. Observe vacuum gauge. Open throttle part way and hold steady. If vacuum gauge reading slowly drops after stabilizing, check exhaust system for restriction.
FUEL SYSTEM
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Check that the following systems and components are in good condition and operating properly before diagnosing problems in fuel injection system:
Check battery condition.
Check all wiring and vacuum connections.
Check air cleaner and ducting.
Check state of tune.
Check fuel delivery system.
Check cooling system.
Check inertia fuel shutoff switch.
Check for hydrostatic lock (liquid in cylinder).
Check fuel tank contents and fuel gauge accuracy.
Check for dirt, water or other contamination in fuel.
Check fuel lines and fittings for leaks.
Check fuel delivery system for proper pressure and volume.
Check for inoperative fuel injectors.
Sunday, April 11th, 2010 AT 7:47 AM



