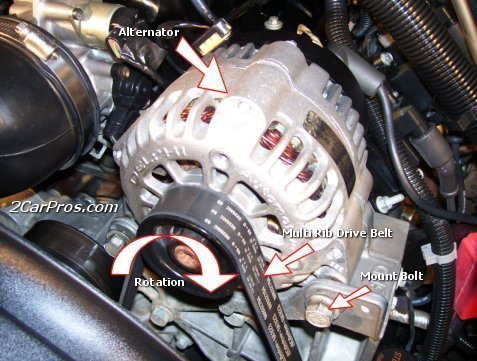
There's a lot more involved with this type of problem. Most simple testers only check that the battery voltage is between 13.75 and 14.75 volts with the engine running. You can do that yourself with an inexpensive digital voltmeter. If that voltage is okay, that only means it is okay to perform the rest of the tests, but you need a professional load tester for that. Specifically, we need to know "full-load output current" and "ripple voltage".
All AC generators have at lest six diodes, and if one fails, all you'll be able to get is exactly one third of the rated output current. 30 amps from the common 90-amp generator is not enough to run the entire electrical system under all conditions. The voltage regulator will detect that missing one third of the output and turn on the "Battery" warning light in response.
If it is necessary to replace the generator, also look at the age of the battery. Due to the design, these generators develop a lot of harmful voltage spikes that can damage those diodes, and the internal voltage regulator, and they can interfere with computer sensor signals. The battery is the key component in damping and absorbing those spikes, but as they age and the lead flakes off the plates, they lose their ability to do that. It is common to go through four to six replacement generators in the life of the vehicle. To reduce the high number of repeat failures, always replace the battery at the same time, unless it is less than about two years old. If it tests good, it can still be used in an '86 or older GM car with the older generator design.
Monday, November 11th, 2019 AT 5:20 PM
(Merged)