TRIGGERING SIGNALS
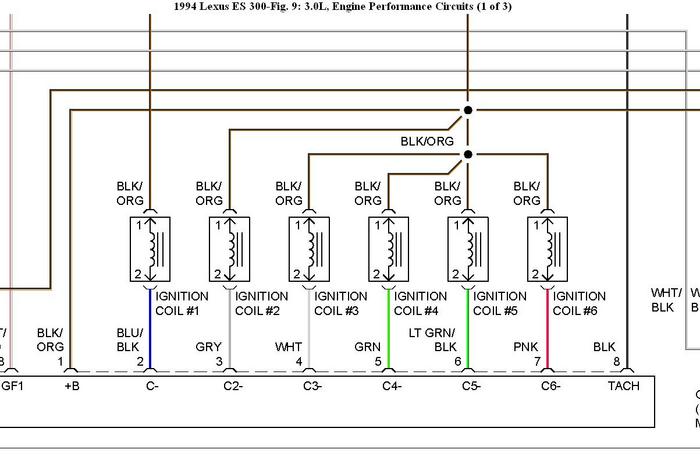
Two camshaft sensors (one camshaft sensor) and a crankshaft sensor provide the triggering signals for the ECM, which uses these signals to control the ignitor(s).
The camshaft sensor contains a pick-up coil. A reluctor is mounted on the camshaft. As the camshaft rotates, a protrusion on the reluctor passes near the pick-up coil. This induces AC voltage in the pick-up coil. ECM interprets this AC voltage signal as TDC of cylinder No. 1.
The crankshaft sensor contains a pick-up coil. A reluctor is mounted on the crankshaft pulley. As the crankshaft rotates, protrusions on the reluctor pass near the pick-up coil. This induces AC voltage in the pick-up coil. The ECM senses the AC voltage, and uses it to determine incremental crankshaft position and engine speed.
IGNITOR(S)
Ignitor keeps the ignition coil primary circuit grounded, allowing a magnetic field to be built up in the ignition coil. When the ECM signals the ignitor, the ignitor interrupts the primary circuit, causing the ignition coil to fire.
Are you sure it is 1, 2 and 4 that is not firing? Recheck wireharness and connectors for loseness and contaminations.
SPONSORED LINKS
Tuesday, January 18th, 2011 AT 3:23 PM