This guide demonstrates how to locate and test the various car electrical fuses that protect particular electrical system accessories. When testing a fuse, there are two aspects to consider. First, the integrity of the fuse is subject to failure. The second is to confirm electrical power is present at the fuse. The second is to test for electrical power at the fuse, if the sub-system that powers the circuit is not working i.e. a bad power relay, maxi or fusible link the fuse will not have power and the accessory will not work.
What goes wrong?
When powering an electrical circuit a designed the amperage to run the accessory is calculated by the engineer. When the amperage pulled through the circuit becomes too excessive the fuse will overheat and blow protecting the circuit or accessory from fire. This condition can occur when a particular accessory wears out or when electrical power connects to the ground of the car for example the body, frame, drive train or interior metal parts. It is important to know that a fuse can fatigue and fail as well.
Where is it?
Most cars are designed with multiple fuse panels which are usually located under the hood, in the interior of the car or in the trunk. These panels are commonly known as the PDC (power distribution center) or fuse and relay panel which can be identified by having a black plastic cover over the top or side of the panel. Each car is different, an owners manual will indicate the location and fuse designation. If you don't know where a particular fuse is located please ask one of our experts and they will help find it for you.
What's the cost?
A fuse replacement is one of the most reasonable cost repairs in the industry. Almost anyone can test and change a fuse for the simple cost of the fuse which is about $2.00 US. This can vary due to fuse size and design, but most are easy to replace.
Let's Get Started
As with any electrical problem its best to inspect which ever accessory is not
working such as a window motor, HVAC system or external lighting is to check all
other accessory operations as well. This is because there are many shared power
sources which can help trace down issues especially in newer vehicles designed with
a BCM (body control module), TIPM (totally integrated power module) or IPDM (intelligent
power distribution module) electrical elements. Turn the ignition key on without
starting the engine to begin. Below is a typical fuse and relay panel under the
hood. Usually you can see several wiring harnesses protruding from the unit.

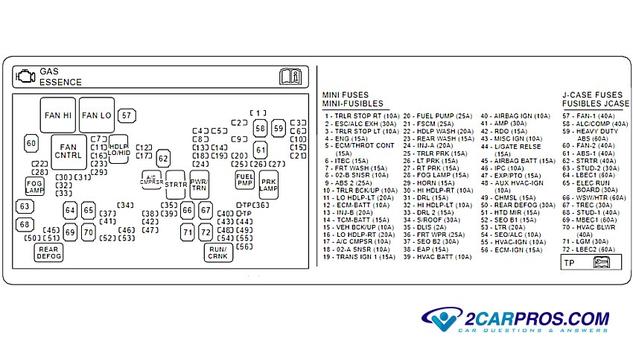
The lid or cover of the fuse panel will in most cases have the fuse and relay
identification illustration depicting what the fuse controls and which amperage
it should be replaced with if blown, or popped as some say. Here is what a typical
fuse and relay legend looks like.
Again, with the key still in the on position start checking for power at all
fuses, ground the test
light and touch the point to the top metal tangs on both sides of the fuse.
A fuse with power on just one side is blown and needs replacement. Note: Some fuses
will not have power on either side due to nonuse of the fuse at the time. When testing
lighting system fuses etc its best to have the system in question turned to the
on position.

Once you have found the bad fuse remove the unit using your fingers or a small
pair of pliers. Sometimes there will be a tool located inside the fuse panel to
help with the removal. This is what a bad fuse looks like compared to a good one.
Replace failed fuses with proper amp rating, not doing so can result in electrical
system damage. Also, fuses can cause intermittent open circuits by becoming loose
or corroded in the fuse holder, make sure fuse is held securely and free from dirt
or corrosion.

Watch the Video!
Please watch this video of the job being done, then continue down the guide to glean additional helpful information.
Good to Know
If the fuse blows when replaced the protected circuit is shorted to ground via either the wire itself or the accessory has failed internally, in either case a repair is necessary to resume normal fuse operation. If no power is detected at the fuse or panel (either side of the all fuses) use a wiring schematic to trace the power source, usually a main power relay, maxi-fuse or fusible link has failed.
Questions?
Our certified technicians are ready to answer fuse test questions for free. We hope you saved money and learned from this guide. We are creating a full set of car repair guides. Please subscribe to our 2CarPros YouTube channel and check back often for new videos which are uploaded regularly.



