Hello,
Ok, from looking through it does not have anything stating device 1 but from what I read I would say that device 1 is the Battery since the code has to do with low voltage. Anyway below are a couple docs with the Code C0899. Hope this helps. If need more let me know.
DTC C0899 (PSCM)
Diagnostic Instructions (PSCM)
� Perform the prior to using this diagnostic procedure.
� Review for an overview of the diagnostic approach.
� provides an overview of each diagnostic category.
DTC Descriptor (PSCM)
DTC C0899 03
Device Voltage Low - PSCM
Diagnostic Fault Information (PSCM)
Circuit Short to Ground Open/High Resistance Short to Voltage Signal Performance
Battery Voltage C0899 03 C0899 03 - -
Ground - C0899 03 - -
Typical Scan Tool Data (PSCM)
Battery Voltage Signal - PSCM
Circuit Short to Ground Open Short to Voltage
Operating Conditions: Ignition ON, Engine OFF. Parameter Normal Value: 12.60 Volts
B+ 0.00 Volts 0.00 Volts 12.60 Volts
Circuit/System Description (PSCM)
The power steering control module (PSCM) monitors the battery voltage available in order to ensure the power steering system has adequate voltage levels to perform the system functions.
Conditions for Running the DTC (PSCM)
The ignition is ON.
Conditions for Setting the DTC (PSCM)
The power steering system voltage is less than 9 volts for 1 second.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets (PSCM)
� No steering assist is provided.
� The driver information center (DIC) displays the POWER STEERING message.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC (PSCM)
� The condition for the DTC is no longer present.
� The PSCM automatically clears the history DTC when a current DTC is not detected in 100 consecutive ignition cycles.
Diagnostic Aids (PSCM)
A low voltage DTC in multiple modules indicates a concern in the charging system.
Reference Information (PSCM)
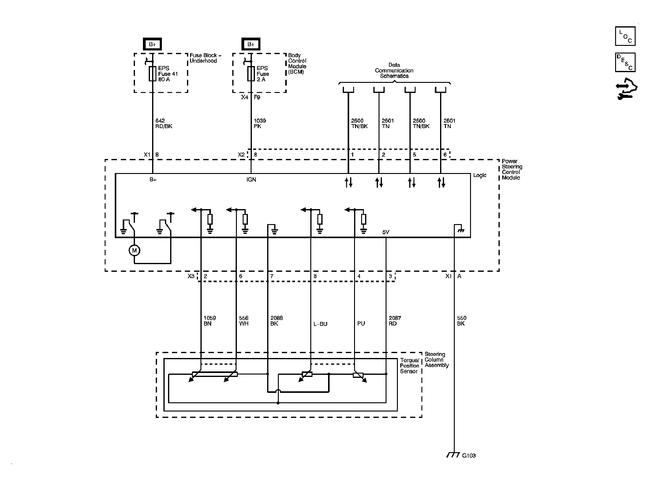
Schematic Reference
Connector End View Reference
Description and Operation
� or
�
Electrical Information Reference
�
�
�
�
Scan Tool Reference
for scan tool information
Circuit/System Verification (PSCM)
1. Engine running, accessories OFF, measure and record the voltage at the battery voltage at the battery terminals. The voltage should be between 12.6 and 15.0 volts.
O If not within the specified range, refer to .
2. Observe the scan tool PSCM Battery Voltage Signal parameter. The reading should be between 12.6 and 15.0 volts.
Circuit/System Testing (PSCM)
1. Ignition OFF, disconnect the harness connector at the PSCM.
2. Ignition OFF and scan tool disconnected, open and close the drivers door, and wait 1 minute. Test for less than 5 ohms between the ground circuit terminal A X1 and ground.
O If greater than the specified range, test the ground circuit for an open/high resistance.
3. Verify that a test lamp illuminates between the B+ circuit terminal B X1 and ground.
O If the test lamp does not illuminate, test the B+ circuit for a short to ground or an open/high resistance.
4. Ignition ON, verify that a test lamp illuminates between the ignition circuit terminal 8 X2 and ground.
O If the test lamp does not illuminate, test the ignition circuit for a short to ground or an open/high resistance.
5. If all circuits test normal, replace the PSCM.
Repair Procedures (PSCM)
Perform the after completing the diagnostic procedure.
For PSCM replacement, setup and programming.
DTC C0899 (EBCM)
Diagnostic Instructions (EBCM)
� Perform the prior to using this diagnostic procedure.
� Review for an overview of this diagnostic approach.
� provides an overview of each diagnostic category.
DTC Descriptor (EBCM)
DTC C0899 00
Device Voltage Low
Diagnostic Fault Information (EBCM)
Circuit Short to Ground Open/High Resistance Short to Voltage Signal Performance
B+ C0899 00 C0899 00 - -
Ground - C0899 00 - -
Typical Scan Tool Data (EBCM)
Battery Voltage Signal - EBCM
Circuit Short to Ground Open Short to Voltage
Operating Conditions: Ignition ON, engine OFF. Parameter Normal Value: 12.60 Volts
B+ 0.00 Volts 0.00 Volts 12.60 Volts
Circuit/System Description (EBCM)
The electronic brake control module (EBCM) monitors the ignition voltage level available for system operation. A low voltage condition prevents the system from operating properly. If the EBCM detects low system voltage, DTC C0899 00 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC (EBCM)
The ignition is ON.
Conditions for Setting the DTC (EBCM)
The EBCM detects that the system voltage is less than 9 volts.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets (EBCM)
� The antilock brake system (ABS) and dynamic rear proportioning (DRP), hydraulic brake assist (HBA), and traction control system (TCS) are disabled.
� The vehicle stability enhancement system (VSES) is disabled, if equipped.
� The ABS, BRAKE, and TRACTION CONTROL OFF indicators turn ON.
� The STABILITY SYSTEM OFF indicator turns ON, if equipped.
� The radio displays the SERVICE TRACTION message.
� The radio displays the ESC OFF and SERVICE ESC messages, if equipped.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC (EBCM)
� The DTC will pass when the EBCM detects that the system voltage is greater than 9.5 volts for 100 msec.
� The EBCM automatically clears a history DTC when a current DTC is not detected in 100 consecutive drive cycles.
� The indicators and radio messages turn OFF when the DTC passes.
Diagnostic Aids (EBCM)
A low voltage DTC in multiple modules indicates a concern in the charging system.
Reference Information (EBCM)
Schematic Reference
Connector End View Reference
Description and Operation
�
�
Electrical Information Reference
�
�
�
�
Scan Tool Reference
for scan tool information
Circuit/System Verification (EBCM)
1. Engine running, accessories OFF, measure and record the voltage at the battery voltage at the battery terminals. The voltage should be between 12.6 and 15.0 volts.
O If not within the specified range, refer to .
2. Observe the scan tool EBCM Battery Voltage Signal parameter. The reading should be between 12.60 and 15.00 volts.
Circuit/System Testing (EBCM)
1. Ignition OFF, disconnect the harness connector at the EBCM.
2. Ignition OFF and scan tool disconnected, open and close the driver door, and wait 1 minute. Test for less than 5 ohms between the ground circuit terminals listed below and ground.
O Terminal 13
o Terminal 38
o If greater than the specified range, test the ground circuit for an open/high resistance.
3. Verify that a test lamp illuminates between the B+ circuit terminal 1 and ground.
O If the test lamp does not illuminate, test the B+ circuit for a short to ground or an open/high resistance.
4. Ignition ON, verify that a test lamp illuminates between the ignition circuit terminal 25 and ground.
O If the test lamp does not illuminate, test the ignition circuit for a short to ground or an open/high resistance.
5. If all circuits test normal, replace the EBCM.
Repair Procedures (EBCM)
Perform the after completing the diagnostic procedure.
For EBCM replacement, setup, and programming.
Wednesday, February 19th, 2014 AT 7:36 PM