A relay is switch that utilizes an electrical trigger signal to activate. Once activated the relay connects an electrical supply to a particular accessory. These accessories can range from the main computer PCM (powertrian control module), radiator fan, fuel pump, door locks etc. There are two tests that should be considered when dealing with a relay problem, is the problem with the relay itself or is the problem a power or ground issue. A relay is prone to failure when used for a long periods of time (hot) or when the amperage of the accessory has increased beyond its designed use.
A rely should be considered as two separate halves, the primary side which utilizes an electromagnet to close the secondary electrical circuit. This electromagnet is activated by a simple power (+) and ground (-) much like a light bulb circuit. The second half of the relay is the "switch" that controls power to a particular accessory like a fuel pump or ignition system. In short, when the primary side of the relay (electromagnet) is activated, it closes the contacts (switch) to supply power to operate the accessory.
Tools and Supplies
- Test light
- Small piece of automotive
- Small automotive bulb and socket
Common Problems
- When a relay warm up as in normal operation, the electrical contacts inside the relay can short circuit causing the electrical flow to stop, when the relay contacts cool it will resume the flow of electricity.
- When excessive amperage has been drawn through a relay circuit it can cause the relay contacts to "stick" not allowing the power to be shut off to the accessory. Example: When an ABS system motor ages it will draw excessive amperage causing the control relay to "stick". This condition will run down the battery until corrected.
- Moisture can get inside a relay hindering the relay operation.
- When testing relay circuits for power, ground is accidentally contacted causing the fuse to fail.
Let's Jump In!
A relay is used to control (switch) a high amperage electrical circuit with a
low amperage one, for example a radiator fan can pull up to 25 amps when in use,
which would burn the computer circuit that controls it, a relay is used to bridge
this circuit to prevent electrical damage.

Before beginning your testing, use a test light and
check all fuses and replace any
that have failed.

Many vehicles supply relay location and identification information on the lid
of the PDC. If this information is not available, please
ask one of our experts to help, its free or check the
owners manual.
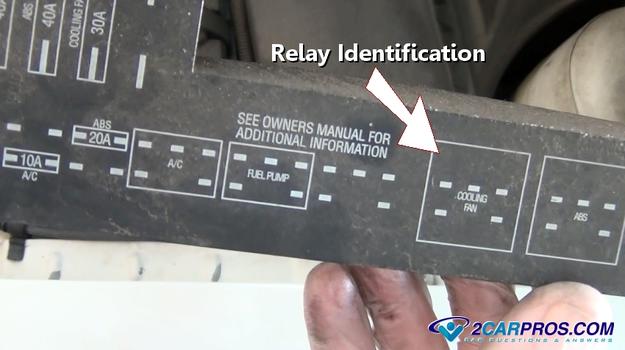
Once the relay has been identified, gently grasp or touch the relay in question,
have a helper turn the ignition key to the on position, then crank the engine over,
the relay should click in one of the ignition switch positions. If so the trigger
circuit of the relay electrical system is working, if not continue to next step.
If the relay clicks and the circuit is still not working there is a good chance
the contacts inside the relay have shorted.

Next, remove the relay for inspection, grasp the relay and pull outward while
slightly wiggling the relay housing, note the orientation of the relay, it must
be installed the correct direction.

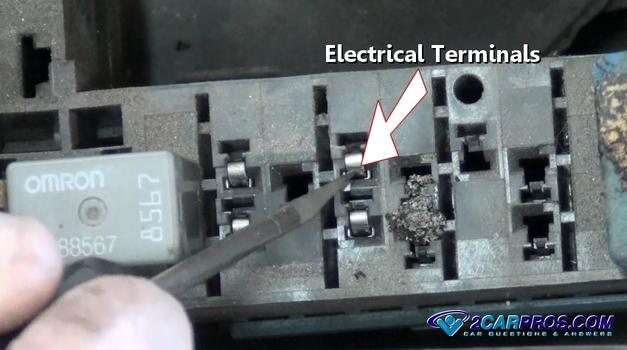
Once the relay has been removed, inspect the relay terminals for signs of extreme
heat or corrosion.

The relay is mounted in four electrical terminals housed in plastic and when
overheated (due to overload or resistance caused by a poor connection) can distort
and melt.

Watch the Video!
Please watch this video of a relay being wired up to help you understand how it works, then continue down the guide to glean additional helpful information.
Use as small metal scribe or tool to scrape clean any corrosion to ensure a good
connection once the new relay is installed.
Most relay's describe the internal circuit by an illustration on the side of the relay.
Relay Terminal Identification
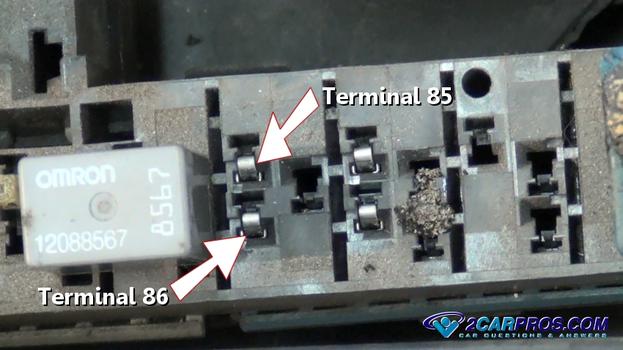
Terminals 86 and 85 are the primary side of the relay, which utilizes an electromagnet to close (connect) the secondary electrical circuit inside the relay. This electromagnet is activated by a simple power (+) and ground (-) much like a light bulb circuit.
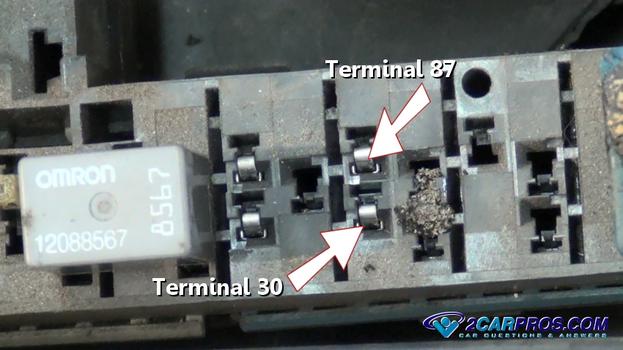
Terminals 87 and 30 are the secondary side of the relay which acts as the "switch" that connects electrical current from one terminal to the other.
Terminal 87a is not widely used and does not need to be connected for the relay to operate. 87a can be used for many different things such as relay activation monitoring or connecting a separate circuit that uses power when the relay is not in use.
Each terminal is identified at the relay base.

To test the trigger or primary side of the relay set up a test light by connecting
a scribe to a test light clamp, being illustrated in the picture below while testing
the tail light socket, just apply this method to the relay terminals.
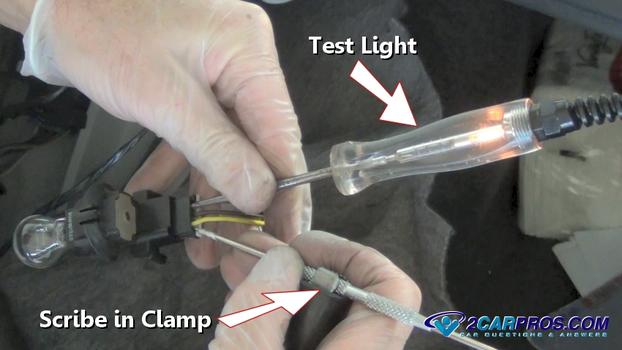
Once the test light is set up connect each end to terminals 86 and 85. Now start
the vehicle and operate the accessory switch, the test light should illuminate,
if not the switch or circuit ground has shorted. ( Note: if the circuit is computer
controlled a delay could be programmed into the operation of the accessory, additionally
if a cooling fan is being tested the engine must reach operating temperature before
the computer will trigger the circuit.) Use the test light grounded to check for
power, and then switch the test light lead to the power side of the battery to check
for circuit ground.
Next, use a piece of wire automotive wire (20 to 16 gauge) and strip both ends
exposing the copper wire. Turn the ignition to the "ON" position and jump terminals
87 and 30 the relay is now jumped and the accessory should activate, if so the relay
has failed. If no power is observed at either 87 or 30, the fusible link or maxi
fuse has shorted. Example: Testing the radiator cooling fan relay, the cooling fan
should be operating.
When replacing a relay be sure to match up the terminal location from the old
relay to to the new unit.

When installing the new relay be sure the orientation is correct or the relay
will not work.

Once proper relay operation has resumed, reinstall the relay (PDC) cover.

Additional Testing
When a particular two wire accessory is not operating, use a grounded test light to check for power at the wiring harness (either wire). If there is no power, the electrical system must be tested starting with the fuse then the relay. If power is present use the test light connected to battery power to check the ground circuit. if these tests check out, the accessory is bad and needs to be replaced.
Some relay's can differ from this configuration but follow the same principle. To confirm the wiring configuration consult a wiring diagram from Google Images or a service manual.
Intermitted Failure
Step 1 - To test for intermitted relay failures which are common, remove the relay in question, take a small wire strand, about two inches long and insert it into the relay connector terminal 87 or 30.
Step 2 - Next, reinstall the relay while keeping the wire strand inserted and clear of any other terminals or metal (ground).
Step 3 - With the wire strand secured in the relay terminal, attach the wire to a small automotive bulb and socket and ground. ( Note: A side marker bulb and socket work great because of its small size, make the wires long enough so the bulb can be seen while driving.)
Step 4 - Temporarily mount the small bulb in a visible area to be seen while driving, masking taped to the hood or dash works well.
Step 5 - This test can be used to test all aspects of the wiring circuitry by moving the bulb ground to power. The bulb will now illuminate when the relay is use, and will go out to signal a failure.
Questions?
Our certified technicians are ready to answer relay testing questions for free. We hope you saved money and learned from this guide. We are creating a full set of car repair guides. Please subscribe to our 2CarPros YouTube channel and check back often for new videos which are uploaded regularly.



